Non fracture dental trauma
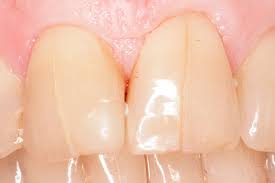
Dental infraction
This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- An incomplete fracture (crack) of the enamel without loss of tooth structure.
- Not tender. If tenderness is observed evaluate the tooth for a possible luxation injury or a root fracture.
Treatment of dental infractions
- In case of marked infractions, etching and sealing with resin to prevent discoloration of the infraction lines. Otherwise, no treatment is necessary.
- No follow up is generally needed.
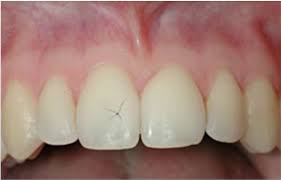
Concussions
This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- The tooth is tender to touch or tapping; it has not been displaced and does not have increased mobility.
Treatment of dental concussions
- No treatment is needed.
- Monitor pulpal condition for at least one year.
- Follow up at 4 weeks, 6-8 weeks, and 1 year.
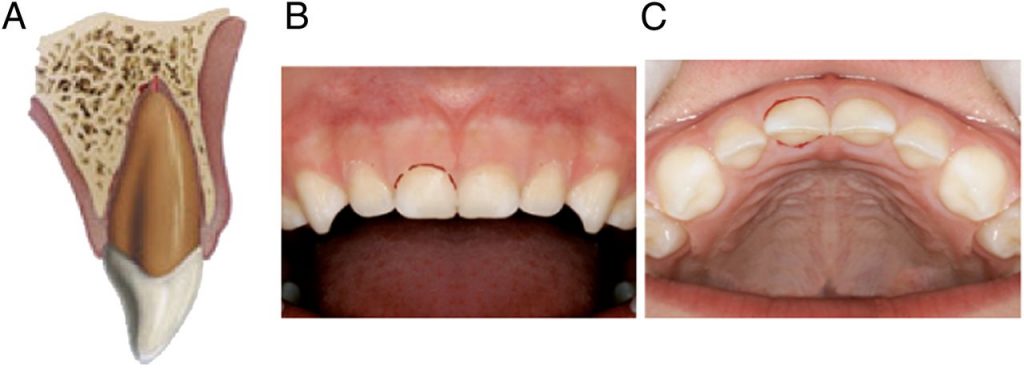
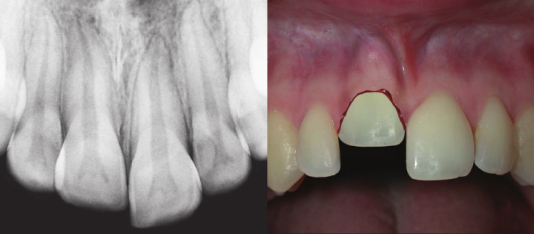
Subluxation
This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- The tooth is tender to touch or tapping; it has not been displaced and does not have increased mobility.
Treatment of subluxation
- No treatment is needed.
- Monitor pulpal condition for at least one year.
- Follow up at 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 6-8 weeks, 6 months, and 1 year.
What are you looking for?
What our clients say

My daughter’s first visit was amazing. The staff are super friendly and informative, the interior is really inviting for kids, and they even gave her a balloon and first visit certificate!
Would 100% recommend.
Would 100% recommend.

My daughter’s first visit was amazing. The staff are super friendly and informative, the interior is really inviting for kids, and they even gave her a balloon and first visit certificate!
Would 100% recommend.
Would 100% recommend.
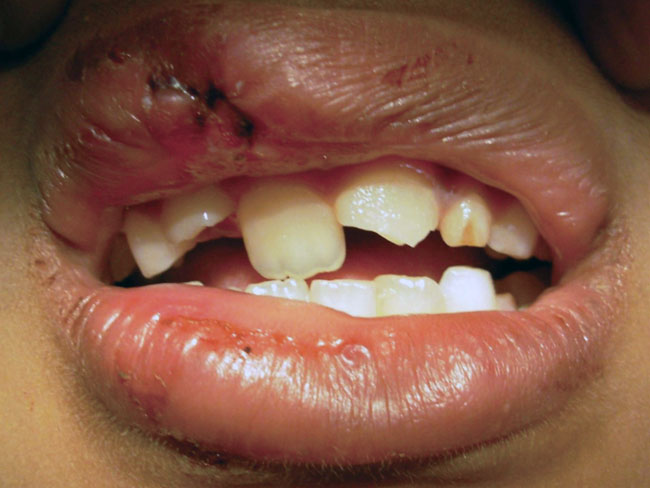
Lateral luxation
The first few hours are very critical. Try to gently move to the teeth back to their position. Use gauze or a napkin to place between the teeth and close the mouth. Visit the dentist immediately. This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- The tooth is displaced, usually in a palatal/lingual or labial direction.
- It will be immobile and percussion usually gives a high, metallic sound.
- Fracture of the alveolar process present.
Treatment of lateral luxations
- Reposition the tooth digitally or with forceps to disengage it from its bony lock and gently reposition it to its original location.
- Stabilize the tooth for 4 weeks using a flexible splint.
- Monitor the pulpal condition.
- If the pulp becomes necrotic, root canal treatment is indicated to prevent root resorption.
- Follow up at 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 6-8 weeks, 6 months, and yearly for 5 years.
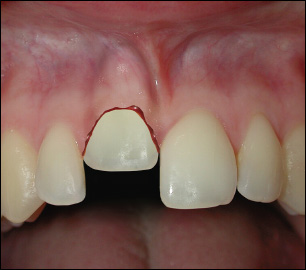
Intrusive Luxation
Intrusive luxaations make the took appear shorter than it actually is. This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- The tooth is displaced axially into the alveolar bone.
- It is immobile and percussion may give a high, metallic (ankylotic) sound.
Treatment of intrusive luxation
- Allow some natural eruption then tailor the treatment to the tooth prognosis.
- Follow up at 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 6-8 weeks, 6 months, and yearly for 5 years.
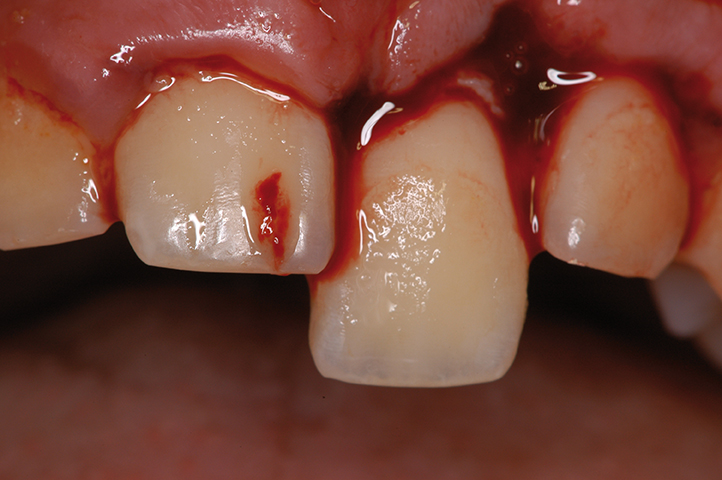
Extrusive luxation
Extrusive luxations make the affected tooth appear longer than it really is. This type of dental trauma is categorized by:
- The tooth appears elongated and is excessively mobile.
Treatment of extrusive luxations
- Reposition the tooth by gently reinserting it into the tooth socket.
- Stabilize the tooth for 2 weeks using a flexible splint.
- In mature teeth where pulp necrosis is anticipated or if several signs and symptoms indicate that the pulp of mature or immature teeth became necrotic, root canal treatment is indicated.
- Follow up at 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 6-8 weeks, 6 months, and yearly for 5 years.
What are you looking for?
What our clients say


