Avulsed (knocked out) teeth
What is a tooth avulsion?
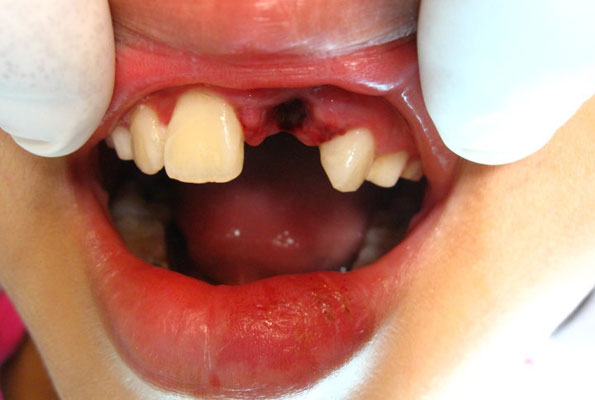
An avulsed tooth is a tooth that has been completely knocked out or removed from its socket. Teeth that have been avulsed can be saved, but require immediate treatment. Your best chance for success for adolescents is within 20 minutes.
Avulsed teeth are a dental emergency. Please see a dental provider immediately.
Can an avulsed tooth be saved?
The short answer is, yes. However, that depends on a number of factors, including time.
The prognosis for avulsed permanent teeth very much depends on the actions taken at the place of the accident. We want to promote and encourage public awareness of first-aid treatment for the avulsed tooth. Treatment choices and prognosis for the avulsed tooth are largely dependent on the vitality of the periodontal ligament (PDL), and the maturity of the root.
Avulsed baby teeth vs. adult teeth
If a baby tooth is avulsed, leave it out of the socket. Next, seek a dentist for a follow-up. Baby teeth should not be replaced; see first aid information below.
If the tooth lost is an adult tooth, you must act quickly in order to save it. Work quickly and calmly through our first aid instructions.
First aid for avulsed teeth
Knocked out teeth are a dental emergency. It’s important that you stay calm and act quickly. First aid begins at the place of the accident. You have about 20 minutes post-accident for the best chance of saving the tooth.
- Most importantly STAY CALM, and keep the child calm.
- If a tooth is avulsed, make sure it is a permanent tooth (primary teeth should not be replanted).
- Find the tooth and pick it up by the crown (the white part). Avoid touching the root.
- If the tooth is dirty, wash it briefly (max 10 sec) under cold running water and reposition it.
- If you are not the child’s guardian, encourage the patient and/or guardian to replant the tooth, if possible. Once the tooth is back in place, bite on a handkerchief to hold it in position.
- If this is not possible, (e.g. an unconscious patient), place the tooth in a glass of milk or another suitable storage medium IMMEDIATELY and bring it with the patient to the emergency clinic.
- The tooth can also be transported in the mouth, keeping it inside the lip or cheek if the patient is conscious.
- If the patient is very young, he/she could swallow the tooth. In this case, it is advisable to get the patient to spit into a container and place the tooth in it. Avoid storage in water.
- If there is access at the place of accident to special storage or transport media (e.g. tissue culture/transport medium, Hanks balanced storage medium (HBSS), or saline solution) such media is preferable and should be used.
- Seek emergency dental treatment immediately.


