What to do about a fractured tooth
If your child has a fractured tooth, it’s important to keep calm. This is not a dental emergency, but your child should see a dentist as soon as possible. If possible, find the broken piece of tooth and store it in water or cold milk.
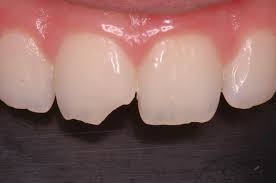
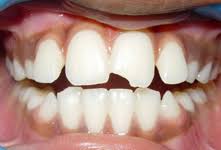
No pain/low pain fractures
Enamel fracture
Most low or no pain fractures are chips to a tooth’s enamel, but cause little to no damage to any of the tooth’s sensitive interior. This type of fracture is categorized by:
- A complete fracture of the enamel.
- Loss of enamel, and no visible sign of exposed dentin.
- Not tender. If tenderness is observed, then evaluate the tooth for a possible luxation or root fracture injury.
Treatment for enamel fractures
- If the tooth fragment is available, we may be able to bond it back in place.
- Treatment consists of contouring or restoration with composite resin, depending on the extent and location of the fracture.
- A follow-up appointment should be made for 6-8 weeks, then again in a year.
Moderate pain and sensitivity fractures
Enamel-dentin fracture
Fractures that cause moderate pain have likely chipped through the enamel and some of the dentin, which is beneath (and protected by) the enamel. This type of fracture is categorized by:
- A fracture confined to enamel and dentin with loss of tooth structure, but not exposing the pulp.
- Normal mobility.
Treatment for enamel-dentin fractures
- Restoration possibly requires some additional medication.
- A follow-up appointment should be made for 6-8 weeks, then again in a year.
Severe pain fractures
Enamel-dentin-pulp fracture
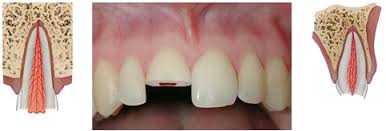
Severe pain likely means the fracture runs deep enough that the innermost part of the tooth has been impacted. Often, fractures of this type will run horizontally or diagonally across the tooth. This type of fracture is categorized by:
- A fracture involving enamel and dentin with loss of tooth structure and exposure of the pulp.
- Redness in the middle of the tooth structure.
Treatment for enamel-dentin-pulp fractures
- Nerve (pulp) needs to be evaluated by the doctor.
- Prognosis is linked to the maturity of the tooth.
- A follow-up appointment should be made for 6-8 weeks, then again in a year.
Crown-root facture
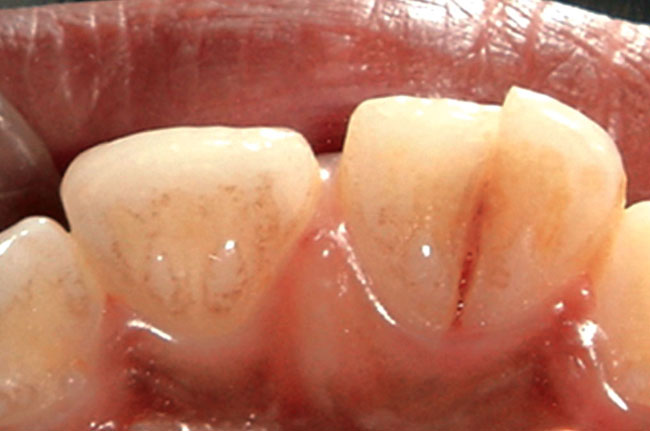
Crown-root fractures tend to run more vertically, and affect the tooth underneath the gum line. This type of fracture is categorized by:
- Crown fracture extending below the gingival margin (gums)
Treatment for crown-root fractures
- Treatments widely vary due to where the fracture ends under the gum/bone.
- Most likely a combination of orthodontic, surgical, restorative, as well as endodontic treatments.
- A follow-up appointment should be made for 6-8 weeks, then again in a year.